0512-67998889(Suzhou)
18051093220(Shenzhen)
"East Wind Sets Off a Thousand Trees of Flowers Overnight | RocRock Biotech Publishes Milestones in Pan-Cancer Macrophage Drug Development"
TME-Induced Tri-TRAIL Macrophage Vector Demonstrates Exceptional Anti-Tumor Power, Achieving Major Breakthroughs in Cancer Treatment. The company's scientific research team's latest development, a paper titled "Tumor micro-environment induced TRAIL secretion from engineered macrophages for anti-tumor therapy," has been published in the international journal of cellular immunology, Cellular Immunology, with Professor Yin Xiushan, the founder of RocRock Biotech, serving as the corresponding author.
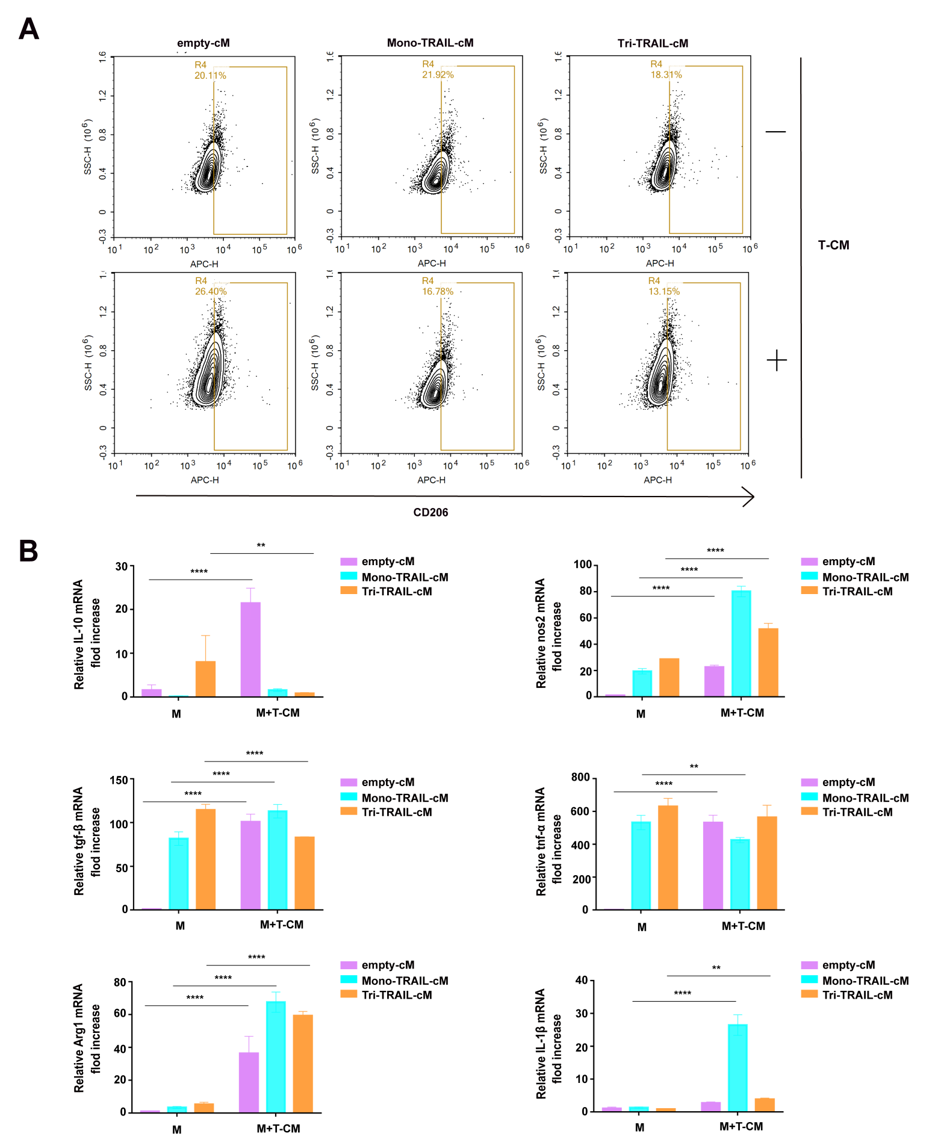
TRAIL, full name Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand, has long been considered a highly promising molecule for targeted cancer therapy. However, its limitations in clinical applications have not been properly addressed. To overcome this bottleneck, RocRock Biotech's scientific research team innovatively developed the Tri-TRAIL-iM macrophage vector, an engineered macrophage that activates under specific conditions of the tumor micro-environment (TME) to precisely release trimeric TRAIL (Tri-TRAIL). The design of Tri-TRAIL-iM cleverly utilizes the natural characteristics of macrophages, making them a TME-responsive drug delivery platform. In vitro and in animal models, Tri-TRAIL-iM showed significant cytotoxicity to tumor cells while having minimal impact on normal cells, highlighting its advantages in improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects. Researchers fused mouse mature TRAIL with the human C-peptide of α1(I) collagen to design Tri-TRAIL-cM. Western blot analysis and flow cytometry confirmed that RAW264.7 cells could efficiently express both forms of TRAIL after lentiviral transduction, with Tri-TRAIL-cM showing significantly higher secretion levels than Mono-TRAIL-cM. ELISA quantitative analysis further confirmed that the concentration of Tri-TRAIL-cM in cell culture supernatants increased over time, especially after 24 hours, its concentration was significantly higher than that of Mono-TRAIL-cM. Annexin V/PI double staining showed that the secretion of TRAIL did not produce toxicity to the vector cells. Further phenotypic studies indicated that under the induction of TME, macrophages secreting TRAIL, especially Tri-TRAIL-cM, significantly downregulated the expression of the M2 (pro-tumorigenic) phenotypic marker CD206 and inhibited the transcriptional activity of IL-10 and TGFβ. These engineered macrophages maintained the activity of pro-inflammatory genes in the TME and highly expressed Arg1, which is consistent with previous research results, highlighting the key role of macrophages in tumor immune regulation.
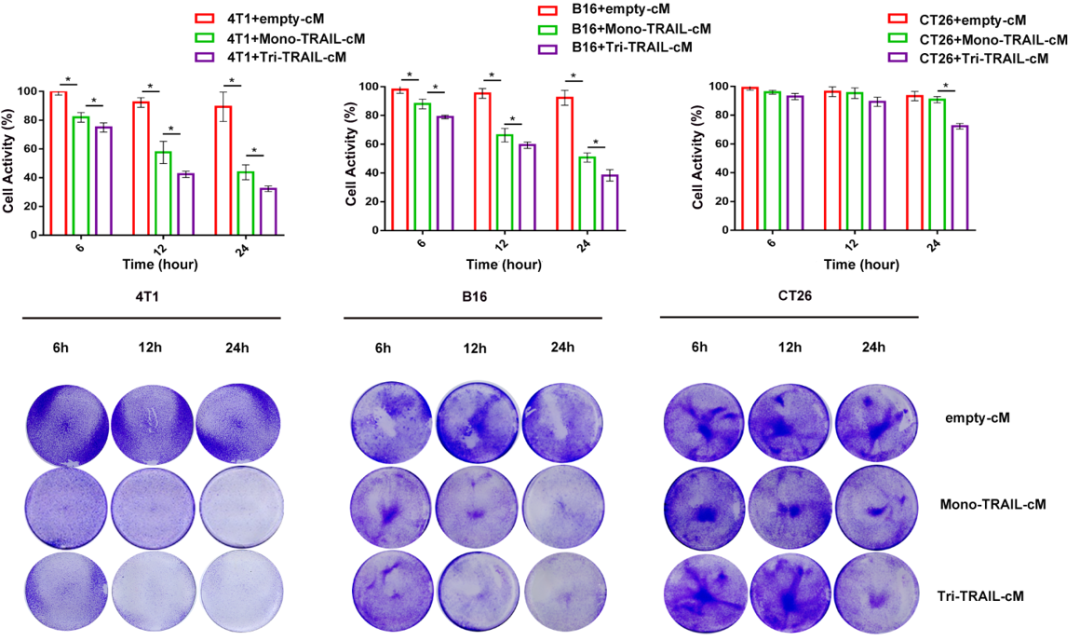
In vitro cellular studies have shown that the conditioned medium of Tri-TRAIL-cM exhibits enhanced cytotoxic activity against tumor cells such as 4T1, B16, and CT26 to varying degrees. This finding confirms the high efficiency of Tri-TRAIL in promoting apoptosis in tumor cells, especially in co-culture experiments, where its apoptotic induction effect on 4T1 cells is more pronounced.
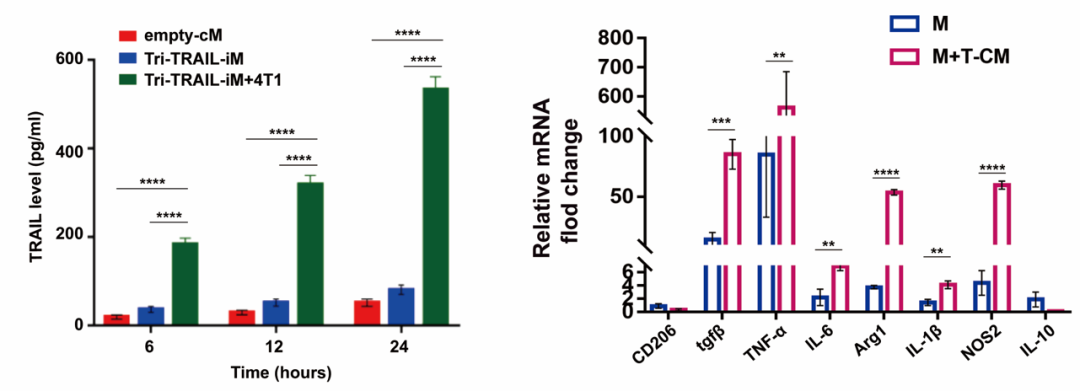
Furthermore, the team utilized the Arg1 promoter to engineer Tri-TRAIL-iM, which exhibits low levels of TRAIL secretion under normal culture conditions. However, upon induction with tumor-conditioned medium (T-CM), the levels of TRAIL significantly increase, demonstrating a specific response to the tumor microenvironment (TME). Under TME stimulation, Tri-TRAIL-iM not only activates the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes but also avoids non-specific cytotoxicity, thereby enhancing its anti-tumor efficacy. This innovative strategy provides a new approach to improving the precision of cancer treatment and reducing side effects.
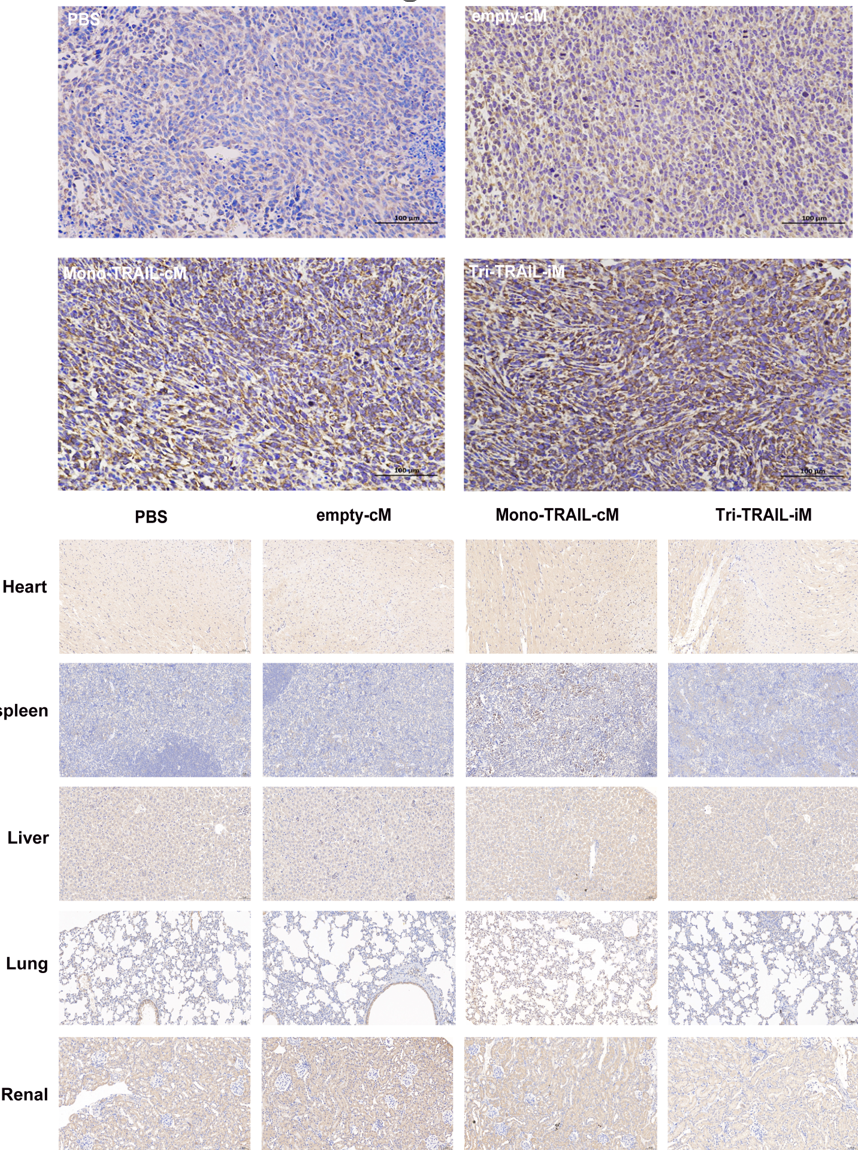
Researchers established a subcutaneous tumor model in mice using 4T1 cells and assessed the expression of Tri-TRAIL-iM in tumor and normal tissues through immunostaining. The experimental results showed that Tri-TRAIL-iM induced a high level of TRAIL expression in tumor tissues, comparable to the Mono-TRAIL-cM group. However, unlike Mono-TRAIL-cM, which also exhibited TRAIL expression in several normal organs, no accumulation of TRAIL was observed in non-tumor tissues with Tri-TRAIL-iM, demonstrating its excellent tumor specificity and potential to reduce side effects on non-tumor tissues.
The macrophage vector Tri-TRAIL-iM has also demonstrated significant antitumor activity and excellent therapeutic safety in a subcutaneous tumor mouse model. Experimental results show that mice treated with Tri-TRAIL-iM experienced a significant slowdown in tumor growth, forming a stark contrast with the PBS control group and the Mono-TRAIL-cM group. Not only did it effectively control the increase in tumor volume, but it also maintained stable mouse body weight in the later stages, highlighting its superior therapeutic index and safety. A deeper histological analysis further revealed the multidimensional benefits of Tri-TRAIL-iM treatment. Tri-TRAIL-iM significantly increased the rate of apoptosis in tumor cells and reduced the expression levels of Ki-67, a marker of cell proliferation, indicating its ability to effectively inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells. In addition, Tri-TRAIL-iM also promoted an increase in the number of iNOS-positive pro-inflammatory macrophages, which not only reflects its positive role in reshaping the tumor microenvironment but also provides key clues for understanding its antitumor mechanisms. In summary, RocRock Bio's latest research confirms that macrophages, as an efficient drug delivery platform in the biomedical field, can accurately deliver Tri-TRAIL to the tumor microenvironment, effectively inhibiting the progression of solid tumors. This innovative strategy not only significantly enhances the targeted killing power against tumor cells, inducing apoptosis, but also protects normal cells to the greatest extent, reducing adverse reactions during treatment. Combining Tri-TRAIL with advanced therapies such as chimeric antigen receptor-engineered macrophages (CAR-M), which specifically recognize and attack tumor cells, can synergistically combat solid tumors. RocRock Bio will continue to delve into this field with the aim of bringing revolutionary treatment options to cancer patients worldwide.
0512-67998889(Suzhou)
18051093220(Shenzhen)

Cathy.Lv@rocrockbio.com(Suzhou)
lliangjing@rocrockbio.com (Shenzhen)